The
SERET project
Aim: To
develop methods for (truck) platooning in complex
topographies
Brief description
In this project, we
are developing (truck) platooning algorithms capable of
handling any form of varying topography, e.g. a hilly
road with rapid slope variation.
Background and
motivation
Platooning
refers to a vehicle configuration in which one or
several vehicles (autonomously) follow a (typically
non-autonomous) lead vehicle, with the aim of reducing
fuel consumption and road congestion, as well as
increasing safety. Such systems being developed by
several vehicle manufacturers, and are likely to appear
in traffic within a few years.
Detailed description
Most (but not all)
work on platooning has been centered on rather
simple topographies, typically flat ground. In
this project, we aim to extend existing
platooning methods, and develop new ones, in
order to handle safe and efficient platooning
in varying topographies. An early result from
this project, whose full name is Safe
Roadtrains for Efficient Transport,
abbreviated SERET) concerns the motion of the
lead vehicle. We have shown that, by
optimizing the set speed (rather than keeping
it constant, as is common) of the lead
vehicle, one can achieve fuel savings of
around 10-15%. In our current work, we are
applying stochastic optimization methods to
improve also the motion of the other vehicles
(the followers) in the platoon.
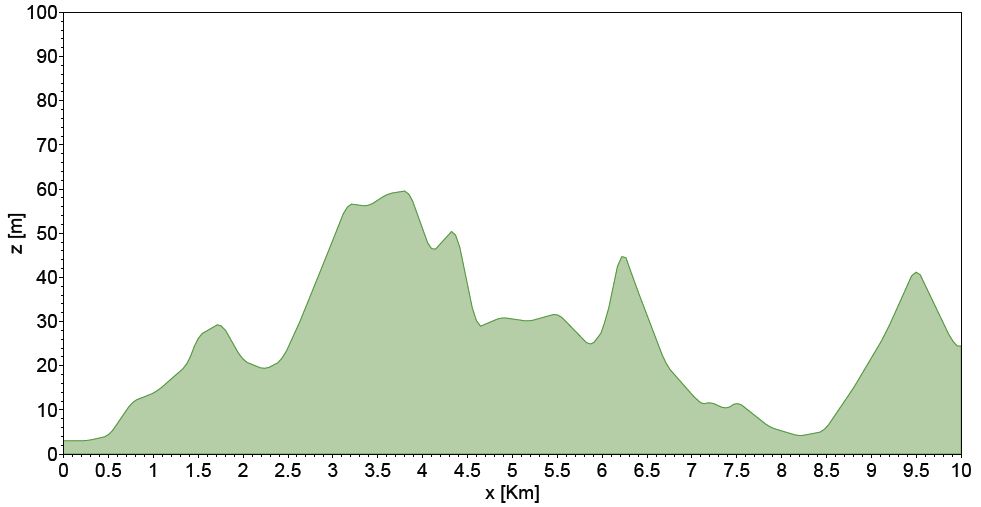
An
example of a typical road topography.
Note that the scale on the z-axis has
been exaggerated by a factor 100.
Participants
Mattias Wahde
Sina Torabi
Last Update:
20150804, 08.00